Conjunctions are a vital grammatical element that connect words, phrases, and clauses to make sentences meaningful. To communicate effectively in English, having a strong knowledge of proper grammar is essential.

In this article, we will discuss the definition, types, structure, and usage of conjunctions with academic examples designed to help students excel in exams and improve their English writing skills.
Prepositions: Rules, Examples, and Easy Usage Guide
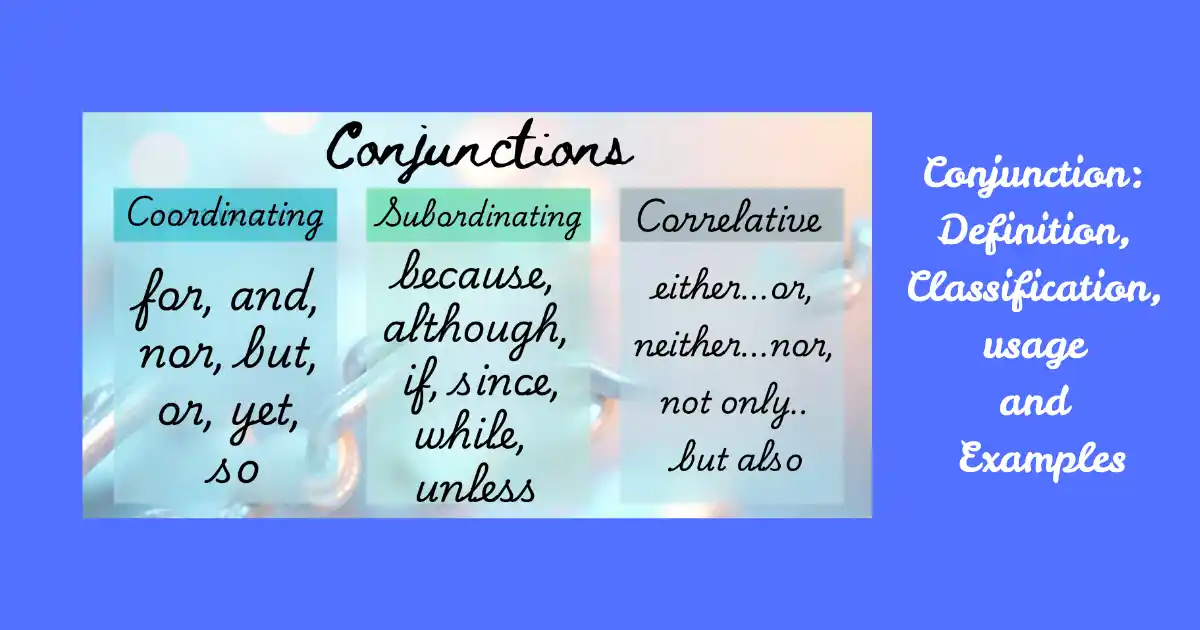
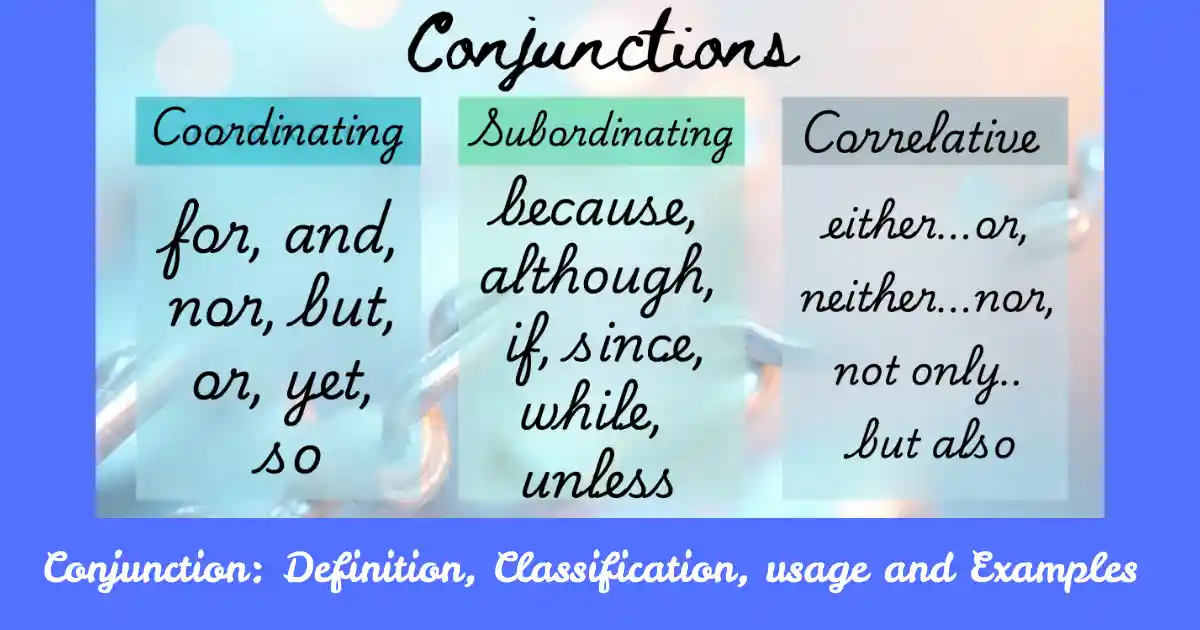
What is a Conjunction?
A conjunction is a word that joins words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence.
Bangla Meaning: Conjunction হল এমন একটি শব্দ যা বাক্যে দুটি বা ততোধিক শব্দ, বাক্যাংশ বা বাক্যকে যুক্ত করে।
Examples (উদাহরণ):
- He is hardworking and honest.
সে পরিশ্রমী এবং সৎ। - I could not attend because I was sick.
আমি আসতে পারিনি, কারণ আমি অসুস্থ ছিলাম।
Conjunction এর প্রকারভেদ:
1. Coordinating Conjunctions
এই ধরণের conjunction দুটি সমমানের শব্দ বা বাক্যাংশ/বাক্যকে যুক্ত করে।
FANBOYS Rule: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
Example:
- I wanted to play, but it was raining.
আমি খেলতে চেয়েছিলাম, কিন্তু বৃষ্টি হচ্ছিল।
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
একটি স্বাধীন বাক্যের সঙ্গে একটি নির্ভরশীল বাক্যকে যুক্ত করে।
Common: because, although, if, since, while, unless
Example:
- Although he studied hard, he failed.
যদিও সে কঠোর পরিশ্রম করেছিল, তবুও সে ব্যর্থ হয়েছে।
3. Correlative Conjunctions
এই ধরণের conjunction যুগ্মভাবে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Examples: either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also
Example: Either you apologize or leave.
হয় তুমি দুঃখ প্রকাশ করো নয়তো চলে যাও।
15 Golden Rules for Using Articles in English Grammar
Conjunction এর গঠন ও ব্যবহার:
Coordinating Conjunctions
Structure: Independent Clause + , + Coordinating Conjunction + Independent Clause
Coordinating conjunctions connect two equal grammatical elements, such as two independent clauses, two phrases, or two words. These are easy to remember using the acronym FANBOYS:
F – For, A – And, N – Nor, B – But, O – Or, Y – Yet, S – So
| Conjunction | ব্যবহার (Usage) | Example Sentence | বাংলা অনুবাদ |
| for | কারণ বোঝাতে (reason) | He stayed home, for he was feeling unwell. | সে বাসায় ছিল, কারণ তার অসুস্থ লাগছিল। |
| and | সংযোজন (addition) | He reads and writes. | সে পড়ে এবং লেখে। |
| nor | নেতিবাচক সংযোজন (negative addition) | He doesn’t smoke, nor does he drink. | সে ধূমপান করে না, এবং সে মদও খায় না। |
| but | বিরোধ বা বিপরীত ধারণা (contrast) | She is poor, but honest. | সে গরিব, কিন্তু সৎ। |
| or | বিকল্প বা অপশন (alternative) | You can have tea, or you can have coffee. | তুমি চা নিতে পারো, নয়তো কফি নিতে পারো। |
| yet | অপ্রত্যাশিত বিরোধ (unexpected contrast) | He is old, yet very active. | সে বৃদ্ধ, তবুও খুব সক্রিয়। |
| so | ফলাফল বা পরিণতি (result) | It rained, so we stayed in. | বৃষ্টি হয়েছে, তাই আমরা ঘরে ছিলাম। |
Subordinating Conjunctions
Structure:
Subordinating Conjunction + Dependent Clause + , + Main Clause
or
Main Clause + Subordinating Conjunction + Dependent Clause
Subordinating conjunctions join a dependent clause to an independent clause. They express time, cause, condition, contrast, or purpose.
| Conjunction | ব্যবহার (Usage) | Example Sentence | বাংলা অনুবাদ |
| because | কারণ | Because I was tired, I slept early. | কারণ আমি ক্লান্ত ছিলাম, আমি তাড়াতাড়ি ঘুমিয়েছি। |
| although | বিপরীত/বিরোধ | Although she is rich, she is humble. | যদিও সে ধনী, তবুও সে বিনয়ী। |
| if | শর্ত | If you study, you will succeed. | যদি তুমি পড়ো, তুমি সফল হবে। |
| when | সময় | When he arrived, the class had started. | যখন সে পৌঁছেছিল, ক্লাস শুরু হয়ে গিয়েছিল। |
| while | একই সময়ে বা বিরোধ | While I was cooking, she was reading. | যখন আমি রান্না করছিলাম, সে পড়ছিল। |
| since | কারণ/সময় থেকে | Since it’s raining, we’ll stay inside. | যেহেতু বৃষ্টি হচ্ছে, আমরা ঘরে থাকব। |
| until | নির্দিষ্ট সময় পর্যন্ত | Wait here until I return. | আমি ফিরে না আসা পর্যন্ত এখানে অপেক্ষা করো। |
| unless | না হলে (negative condition) | You won’t pass unless you work hard. | তুমি কঠোর পরিশ্রম না করলে পাশ করতে পারবে না। |
| as | যেমন/কারণ | As I was leaving, he arrived. | যেহেতু আমি বের হচ্ছিলাম, তখনই সে এলো। |
| even though | তীব্র বিরোধ | Even though it was cold, he didn’t wear a jacket. | যদিও ঠান্ডা ছিল, তবুও সে জ্যাকেট পরেনি। |
| before | পূর্বে | Before the sun rises, we’ll leave. | সূর্য ওঠার আগে, আমরা রওনা হব। |
| after | পরে | After he finished dinner, he went to bed. | ডিনার শেষ করার পরে, সে ঘুমাতে গেল। |
| so that | উদ্দেশ্য/কারণ | I study hard so that I can succeed. | আমি কঠোর পরিশ্রম করি যাতে আমি সফল হতে পারি। |
| as long as | যতক্ষণ পর্যন্ত (শর্তযুক্ত সময়) | You can play as long as you finish your homework. | তুমি খেলতে পারো যতক্ষণ না তুমি হোম ওয়ার্ক শেষ করো। |
| though | বিরোধ | Though he tried hard, he didn’t win. | যদিও সে কঠোর চেষ্টা করেছিল, তবুও জিতেনি। |
Correlative Conjunctions
Structure:
Correlative Pair + Parallel Sentence Elements (same grammatical structure)
Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs to join equal elements of a sentence — such as two nouns, two adjectives, or two clauses — while showing a specific relationship (choice, contrast, emphasis, etc.).
| Correlative Conjunction | Example Sentence | বাংলা অনুবাদ |
| either…or | Either he will come or he will call. | হয়তো সে আসবে নয়তো ফোন দেবে। |
| neither…nor | Neither the teacher nor the students were present. | না শিক্ষক না শিক্ষার্থীরা উপস্থিত ছিলেন না। |
| not only…but also | Not only did he sing, but also danced. | সে শুধু গানই গায়নি, বরং নেচেছেও। |
| both…and | She is both intelligent and hardworking. | সে একই সাথে বুদ্ধিমতী এবং পরিশ্রমী। |
| whether…or | I don’t know whether he will come or not. | আমি জানি না সে আসবে কি আসবে না। |
| as…as | He is as tall as his father. | সে ততটাই লম্বা যতটা তার বাবা। |
| no sooner…than | No sooner had he entered than it started raining. | সে প্রবেশ করতে না করতেই বৃষ্টি শুরু হলো। |
| scarcely…when | Scarcely had I reached home when the phone rang. | আমি ঘরে পৌছুতে না পৌছুতেই ফোনটা বাজল। |
| such…that | He was such a good player that he won the match. | সে এতটাই ভালো খেলোয়াড় ছিল যে ম্যাচ জিতেছিল। |
| so…that | She is so tired that she can’t move. | সে এতটাই ক্লান্ত যে নড়াচড়াও করতে পারছে না। |
| rather…than | I would rather walk than wait for the bus. | আমি বাসের জন্য অপেক্ষা করার চেয়ে হাঁটতে পছন্দ করি। |
অন্য Parts of Speech কীভাবে Conjunction হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়:
Conjunctive Adverbs (সংযোগকারী ক্রিয়া বিশেষণ)
These link independent clauses with a semicolon.
Examples: however, therefore, hence, nevertheless
Example:
- The data is incomplete; therefore, the conclusion is invalid.
তথ্য অসম্পূর্ণ; অতএব, সিদ্ধান্তটি অকার্যকর।
Prepositional or Phrasal Conjunctions
Examples: as long as, even though, so that
Example:
- Even though it was late, he finished the assignment.
যদিও দেরি হয়েছিল, সে কাজটি শেষ করেছে।
Conclusion:
Conjunction শুধুমাত্র ব্যাকরণিক উপাদান নয়, এটি একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ যোগসূত্র যা বাক্যের অর্থ প্রকাশে গভীরতা আনে। একাডেমিক লেখালেখি, প্রেজেন্টেশন, এবং পরীক্ষায় সফল হতে হলে conjunction এর যথাযথ ব্যবহার শেখা জরুরি। আপনি যদি এই গাইডটি অনুশীলন করেন, তবে নির্ভুল ও প্রাঞ্জল ইংরেজি লেখার পথে অনেকদূর এগিয়ে যেতে পারবেন।
Conjunction কাকে বলে? এটি কত প্রকার ও কি কি?
Quiz: Test Your Understanding of Conjunctions:
1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct answer.
Q1: Which of the following is a coordinating conjunction?
a) Because
b) Although
c) But
d) Unless
Q2: Identify the subordinating conjunction in the sentence:
“I will call you after I arrive.”
a) after
b) I
c) will
d) you
Q3: Which pair is a correct correlative conjunction?
a) either…or
b) because…so
c) but…and
d) although…if
2. Fill in the Blanks
Fill the blanks with appropriate conjunctions from the options provided.
Q4: I wanted to go out, _____ it started raining.
(Options: and / but / so)
Q5: She is hardworking, _____ she doesn’t get tired easily.
(Options: because / and / although)
Q6: You can have tea _____ coffee, but not both.
(Options: either / neither / so)
3. True or False
Write True or False.
Q7: The conjunction “unless” is used to show a condition.
Q8: “But” is a subordinating conjunction.
Q9: “Neither…nor” is a pair of correlative conjunctions.
4. Identify the Conjunction Type
In the following sentences, identify the type of conjunction used (Coordinating / Subordinating / Correlative).
Q10: I will wait here until you come.
Q11: She sings and dances beautifully.
Q12: Either you study hard or you fail.
5. Sentence Rewriting
Rewrite the sentence using the conjunction given in brackets.
Q13: I am tired. I will finish my homework later. (Use “because”)
Q14: He didn’t study. He passed the exam. (Use “although”)
Q15: You can come now. You can come later. (Use “either…or”)
6. Create Your Own Sentences
Write one sentence each using the following conjunctions:
Q16: but
Q17: because
Q18: neither…nor
7. Error Correction
Find and correct the error related to conjunction use in the sentence.
Q19: She is both smart and she works hard.
Q20: I will call you if I will arrive on time.

